By [Beijing Tianrun Yi’an Water Purification Equipment Co., Ltd.] | Jul. 9th, 2025
1. Reverse Osmosis and the Water Crisis of 2025
Reverse osmosis is at the forefront of modern water purification technologies, alongside nanofiltration (NF) and ultrafiltration (UF). As of 2022, 2.2 billion people still lacked access to safely managed drinking water, and by 2025, nearly 1.8 billion people are expected to live in areas facing absolute water scarcity. (Sources: UN SDG Report 2024– Clean water and sanitation; FAO & UN Water– Water scarcity)
Against this urgent backdrop, the demand for efficient, reliable water treatment is rising across homes, industries, and municipalities. Choosing the right membrane technology—Reverse Osmosis (RO), Nanofiltration (NF), or Ultrafiltration (UF)—can significantly impact water quality, cost, and system performance.
In this article, the engineering team at Beijing Tianrun Yi’an Water Purification Equipment Co., Ltd. offers a practical comparison of these technologies, supported by application insights and real-world engineering experience. Let’s explore which solution fits your unique needs for 2025 and beyond.
2. Understanding the Three Core Membrane Technologies
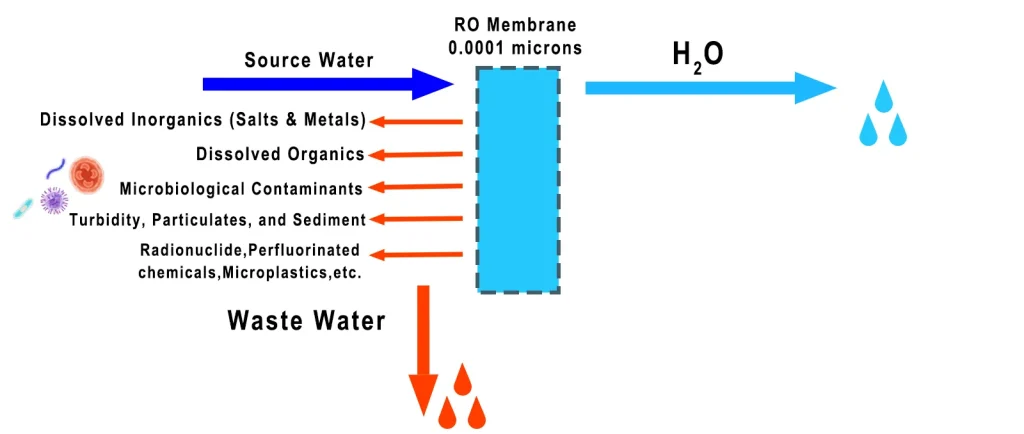
Reverse osmosis (RO) forces water through a semi-permeable membrane with pores around 0.0001 microns, removing over 99% of dissolved solids and contaminants.
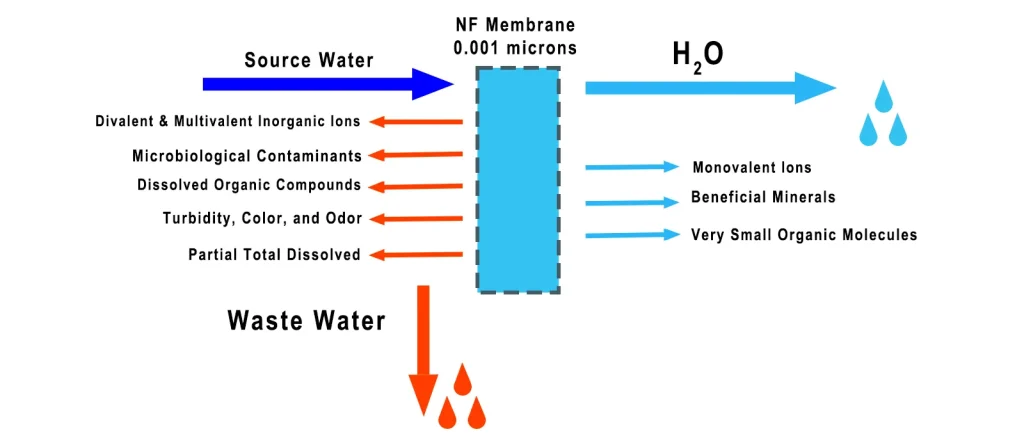
Nanofiltration (NF) operates at slightly lower pressure and filters particles with diameters of around 0.001 microns. It retains some beneficial minerals while removing organic compounds and divalent salts.
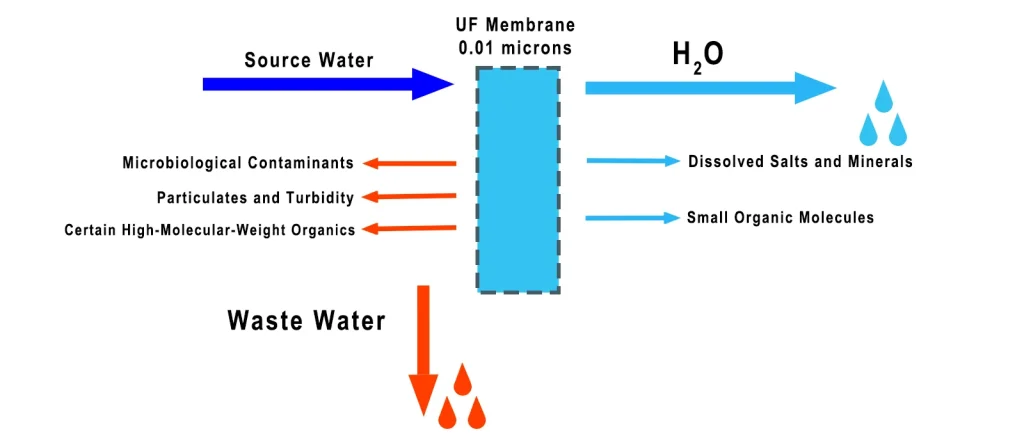
Ultrafiltration (UF) uses membranes with pores of ~0.01 microns to remove bacteria, viruses, and suspended solids, but not dissolved salts.
3. Key Comparison Table: Reverse Osmosis vs. Nanofiltration vs. Ultrafiltration
| Feature | RO | NF | UF |
| Pore Size | ~0.0001 μm | ~0.001 μm | ~0.01 μm |
| Removes TDS | ✅(>95%) | ⚠️Partial(50~90%) | ❌ (<10%) |
| Removes Bacteria/Viruses | ✅ | ✅Partial ( >99.9%) | ✅Excellent bacteria / Partial viruses |
| Removes Minerals | ❌ | ⚠️Partial (Retains beneficial minerals) | ✅Keeps all |
| Pressure Needed | High(50-1000+ psi) | Medium(35-60 psi) | Low (gravity/electric) |
| Energy Use | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate | Low |
| Wastewater Generated | Yes(30-50%) | Minimal (10~25%) | Minimal (<10%) |
| Best For | Pure water, desalination, etc. | Pure water, desalination,etc. | Microbiological safety,etc. |
Actual values vary with feed quality and operation cycles (e.g., backwash frequency). References: ISO 20468-5:2021 (Water treatment membranes —Guidelines for performance evaluation of treatment technologies for water reuse systems Performance criteria), AWWA M53 Sec 9.4 (Microfiltration and Ultrafiltration Membranes for Drinking Water), DuPont UF Design Manual.
4. Applications of Each Technology
• Reverse Osmosis: Desalination, ultrapure industrial water, bottled water, high-TDS residential water, etc.
• Nanofiltration: Water softening, pre-RO treatment, municipal water conditioning, biotech processing, etc.
• Ultrafiltration: Tap water polishing, off-grid rural systems, pre-filtration, emergency kits, etc.
5. Reverse Osmosis in Action: Real-World Use Cases
In coastal regions such as Shandong, China, and Dubai, UAE, reverse osmosis has become the backbone of large-scale desalination systems. These facilities convert seawater into drinking water for millions using energy-efficient and smart membrane technologies.
6. Future Trends: What’s Next for Water Filtration?
In recent years, water treatment technologies such as reverse osmosis (RO) have been drawing attention from both residential and industrial sectors. Many industry observers anticipate that, between 2025 and 2030, demand for RO solutions could continue to expand as communities address challenges like limited freshwater resources, rapid urban development, and the push toward greener infrastructure. Emerging approaches — including hybrid RO configurations, solar-powered operations, and intelligent monitoring systems — are increasingly viewed as promising directions for improving efficiency and sustainability.
7. FAQ: Your Most Common Questions
❓ Can I install UF instead of RO at home?
Yes—if your water is already low in TDS and you want to retain minerals. UF is also ideal for cities with treated municipal water but older piping systems.
❓ Is RO water safe for daily drinking?
Yes. While it removes minerals, many systems today include post-filters that add essential minerals like calcium and magnesium back into the water.
❓Is reverse osmosis eco-friendly?
Newer systems minimize wastewater and support water-saving features.
❓ How often do membranes need to be replaced?
- RO: every 2–3 years
- NF: every 1.5–2 years
- UF: every 12 months (or based on usage and water quality)
8. Our Water Solutions: Built for Your Needs
At Beijing Tianrun Yi’an, we provide end-to-end solutions for residential, commercial, and industrial water purification. Whether you’re a distributor looking for OEM/ODM systems or a business in need of reliable large-scale purification, we engineer systems that integrate:
- Smart RO/NF/UF combinations
- Solar-powered UF solutions for rural areas
- Brackish water desalination plants
- Customized pre-filtration and post-treatment stages
- Certified components meeting global standards
🔗 [Explore Our Product Series →Home & Workplace Water Purifier]
📩 Need Expert Guidance?
We offer free water quality consultations. Upload your water test report, and our engineers will provide a tailored system design to match your needs and local compliance requirements.


